Section One - Fundamentals
01
Camera Basics
Students will learn camera basics including types of cameras, and how a camera functions. Students will learn about full frame versus crop sensor camera and why a DLSR camera is a better choice for crime scene photography versus a cellphone camera or a point and shoot.
02
Lenses and Focal Lengths
Students will learn about lenses and focal lengths. Students will learn what lenses to use for what situations and what problems can arise from lens distortion and compression. Students will learn to understand the properties of a lens based on the information displayed on the lens.
03
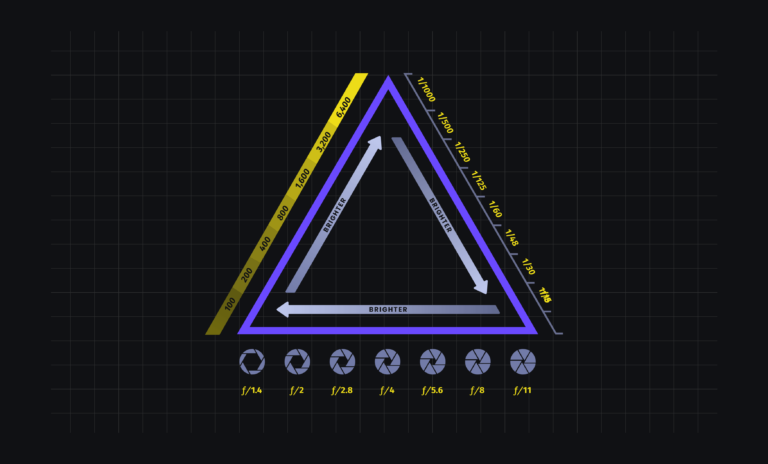
Exposure Triangle
Students will learn how to read a light meter and about the %18 grey principle. Students will be introduced to the exposure triangle which are the three settings they can change to correctly expose a photo.
04
Shutter speed
The first leg of the exposure triangle is shutter speed. Students will learn how the shutter operates and how different shutter speeds can affect their photo. Students will learn how to recognize and read shutter speeds on their cameras.
05
Aperture
The second leg of the exposure triangle is aperture. Aperture controls the amount of light which enters the camera and the depth of field of a photo. Lens flare and diffraction can be affected by aperture.
06
ISO
ISO is the third leg of the exposure triangle. Students will learn the drawbacks of choosing a higher ISO and when it is appropriate and unavoidable to use a higher ISO. Students will learn about noise introduced into photos through ISO and why it’s there.

07
Putting it all together
Students should understand how the exposure triangle works and be able to incorporate the previous lessons into a comfortable working knowledge of using their cameras in manual mode. Students will know how to use all the modes of their camera.
“It’s not enough to just own a camera. Everyone owns a camera. To be a photographer, you must understand, appreciate, and harness the power you hold!” - Mark Denman
Section 2 - Advanced Photography
08
Focus
Students will be taught the difference between focus modes and how they work. Students will be introduced to focus points and back button focus which are essential in crime scene photography. Lens stabilization will be introduced and students will know when to use or turn off stabilization.
09
Metering
Students will learn what light metering is and the various modes each camera is equipped with. Students will learn how each mode works and what effects it may have on their photos. Students will learn the relation between metering and the 18% grey principle.
10
White balance and drive modes
Students will be introduced to the drive modes of their cameras and self timers which are essential for crime scene photography. Students will learn about the Kelvin temperature of light, and their effects on photos. Students will learn how to correct white balance both on scene and during post processing.
11
Composition
Composition is where art meets function. There is a difference between a photograph and a great photograph. Understanding what the eye finds pleasing will help students create photographs which jurors will find compelling and tell the story of their scene more convincingly.
12
Lighting
Photography is about capturing light. The quality of light can positively or negatively impact photos. Understanding light and how to manipulate it is a critical skill for photographers. Students will learn about camera flash, and light metering.
13
Macro Photography
Macro photography is a critical skill for crime scene photographers. Macro photography introduces depth of field issues, and lighting issues. Focal lengths and reproduction ratios will be covered.
Section 3 - Post Processing

14
The art of Editing
Photographs taken as JPEGS lose 75% of the information captured by the camera. Capturing an image in RAW format can preserve evidence otherwise lost. RAW files require post production editing. Students will learn the proper way to store files and edit them so the information can be admissible in court, and to enhance element of a scene that might otherwise be lost.

“The camera has always been a guide, and it’s allowed me to see things and focus on things that may be an average person wouldn’t even notice.” - Don Chadwick
Section 4 - Crime Scene Photography
15
Crime Scene Photography
A crime scene photo tells a story words can’t properly convey. A crime scene photo can also be examination evidence which allows short lived or delicate evidence to be preserved for further review and testing. Students will understand why we take crime scene photos and understand the elements of a good crime scene photo.
16
Advanced Techniques
Photography can include some advanced techniques such as Focus Stacking, High Dynamic Range (HDR), and Panoramas. Students will learn how to use all of these techniques to overcome difficult situations or to more fully document a scene.
17
Tools
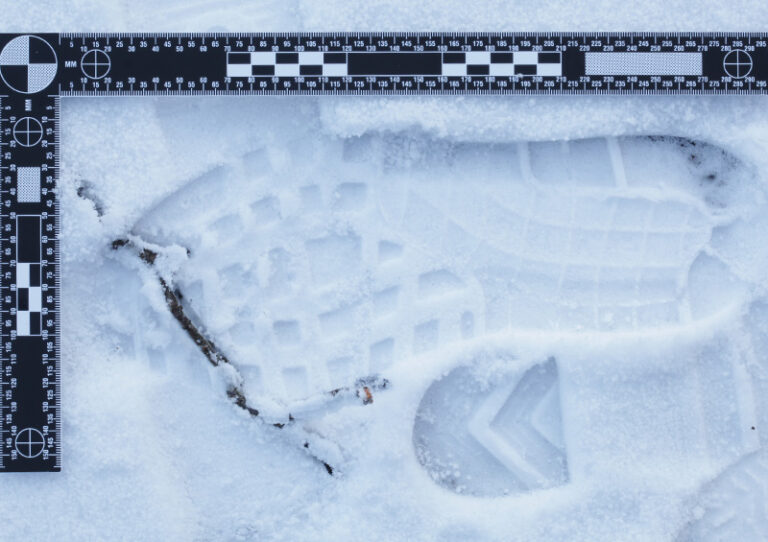
Students will learn what tools they may need or use for crime scene photography including scales, rulers, and lighting equipment. Students will lean how to make and use improvised tools when certain tools aren't available.
18
Scene and Subject Lighting
Students will learn about scene and subject lighting and how to properly illuminate a scene. Students will learn about the dynamic range of a camera, and how to light problematic scenes. Long exposure photography will be covered including painting with light.
19
Best Practices
Every photograph stores meta data. Students will learn how to read and access photo meta data. Students will understand the importance of shooting on a parallel plane and how perspective can distort an evidence photo degrading it's usefulness as examination evidence. Best practices will be discussed for storing evidence photos, and other elements of crime scene photography.
20
Examination Evidence
Examination evidence delves deep into the methodology of extremely challenging crime scene photography. Students will learn how to photograph reflective surfaces, Bluestar, Impressions in snow, impressions in dirt, bloodstains, and more.

21
Case Law and Court Preparation
Students will learn what the legal standard is for photographs entered into evidence, and case law surrounding photographic evidence. Students will learn how an edited photo is admissible in court and what can make an edited photo inadmissible in court.

